
Friday, 16th July, 2021
7.30 PM Chennai
4.00 PM Barcelona
Prof. Antonio Rodriguez-Ferran
Professor
Department of Civil Engineering
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya
Computational modelling of crack branching and merging
Abstract: Continuous-discontinuous computational models of fracture combine a diffuse and a sharp representation of cracks. In the continuous model (e.g. gradient damage models, phase-field approaches), stiffness degradation is represented by a damage parameter. In the discontinuous model, a sharp crack is represented as a jump in the displacement field (e.g. cohesive zone models, XFEM).
Such hybrid computational strategies are especially suitable to model crack branching and merging. A phase-field model captures crack branching in a natural way, and the branching damage field drives the branching topology of the sharp crack. There is no need to rely on ad-hoc, crack-tip-based branching criteria. A similar comment applies to merging.
We will discuss these ideas in the framework of a recently proposed combined XFEM phase-field computational model. We will deal both with the computational aspects (automatic adaptive refinement of the finite element mesh in the crack tips; transition from diffuse cracks to sharp cracks) and with the modelling capabilities for complex crack patterns.
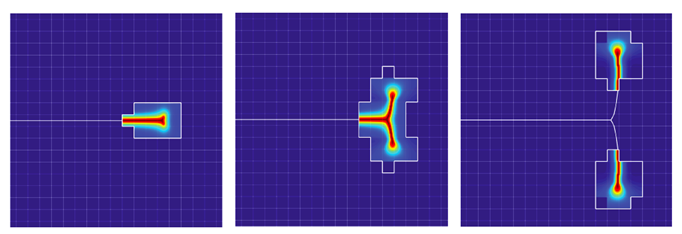
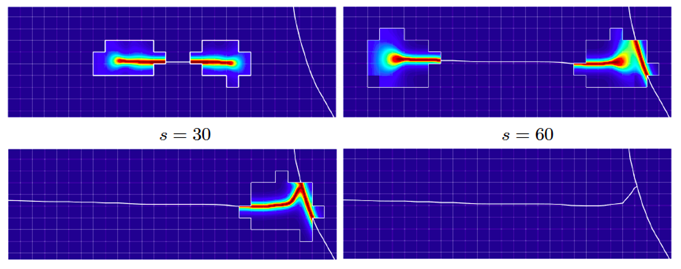
Such hybrid computational strategies are especially suitable to model crack branching and merging. A phase-field model captures crack branching in a natural way, and the branching damage field drives the branching topology of the sharp crack. There is no need to rely on ad-hoc, crack-tip-based branching criteria. A similar comment applies to merging.
We will discuss these ideas in the framework of a recently proposed combined XFEM phase-field computational model. We will deal both with the computational aspects (automatic adaptive refinement of the finite element mesh in the crack tips; transition from diffuse cracks to sharp cracks) and with the modelling capabilities for complex crack patterns.

Crack branching
